RAID Technology
Explanations of the RAID modes used and comparative DataCAM RAID 10 vs Standard RAID 5
RAID is a set of techniques that allow data to be distributed over several hard drives in order to enhance the security, speed and reliability of computers.
The acronym RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
Explanations of the RAID modes used and comparative DataCAM RAID 10 vs Standard RAID 5
RAID is a set of techniques that allow data to be distributed over several hard drives in order to enhance the security, speed and reliability of computers. The acronym RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
Explanations of the RAID modes used and comparative DataCAM RAID 10 vs Standard RAID 5
RAID is a set of techniques that allow data to be distributed over several hard drives in order to enhance the security, speed and reliability of computers.
The acronym RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
RAID 5
ADVANTAGES :
– RAID 5 is one of the most common RAID configurations and is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations.
– Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit. This RAID configuration also offers inexpensive data redundancy and fault tolerance. Writes tend to be slower, because of the parity data calculation, but data can be accessed and read even while a failed drive is being rebuilt. When drives fail, the RAID 5 system can read the information contained on the other drives and recreate that data, tolerating a single drive failure.
DISADVANTAGES :
Longer rebuild times are one of the major drawbacks of RAID 5, and this delay could result in data loss. Because of its complexity, RAID 5 rebuilds can take a day or longer, depending on controller speed and workload. If another disk fails during the rebuild, then data is lost forever.
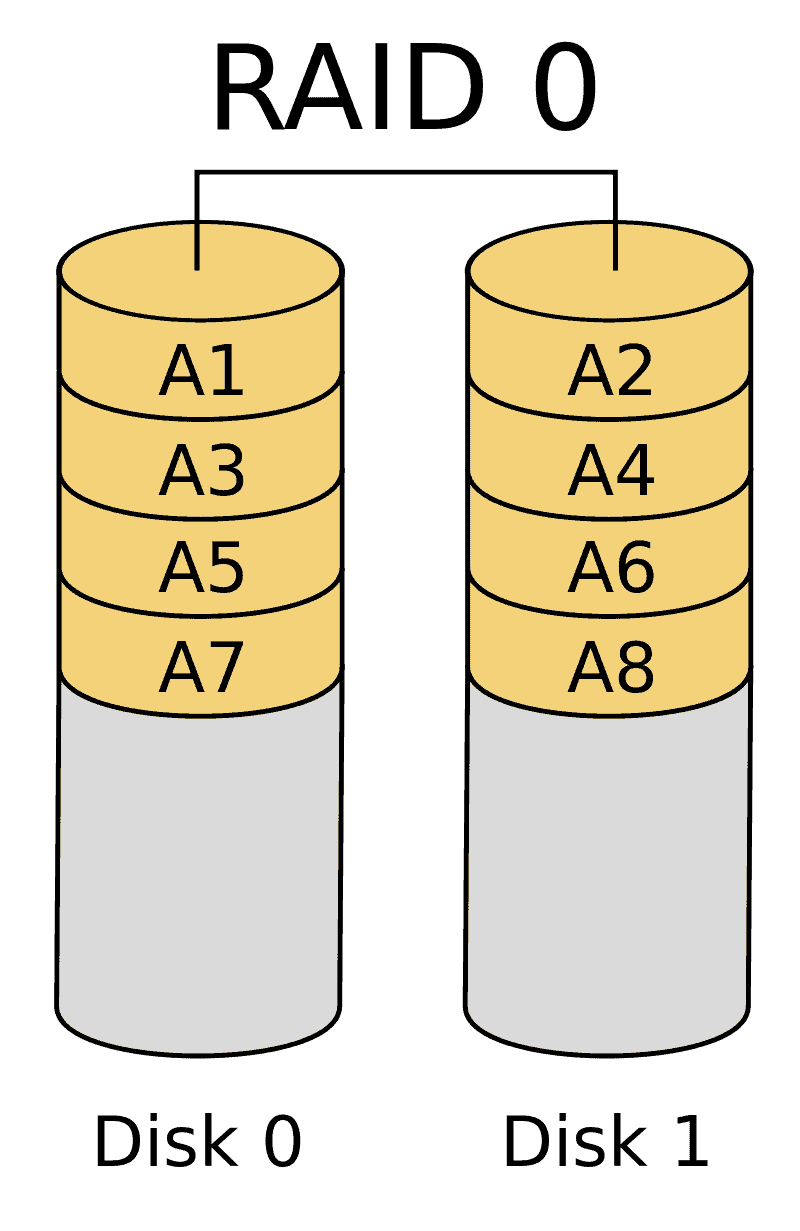
RAID 5
ADVANTAGES :
– RAID 5 is one of the most common RAID configurations and is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations.
– Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit. This RAID configuration also offers inexpensive data redundancy and fault tolerance. Writes tend to be slower, because of the parity data calculation, but data can be accessed and read even while a failed drive is being rebuilt. When drives fail, the RAID 5 system can read the information contained on the other drives and recreate that data, tolerating a single drive failure.
DISADVANTAGES :
Longer rebuild times are one of the major drawbacks of RAID 5, and this delay could result in data loss. Because of its complexity, RAID 5 rebuilds can take a day or longer, depending on controller speed and workload. If another disk fails during the rebuild, then data is lost forever.

RAID 5
ADVANTAGES :
– RAID 5 is one of the most common RAID configurations and is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations.
– Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit. This RAID configuration also offers inexpensive data redundancy and fault tolerance. Writes tend to be slower, because of the parity data calculation, but data can be accessed and read even while a failed drive is being rebuilt. When drives fail, the RAID 5 system can read the information contained on the other drives and recreate that data, tolerating a single drive failure.
DISADVANTAGES :
Longer rebuild times are one of the major drawbacks of RAID 5, and this delay could result in data loss. Because of its complexity, RAID 5 rebuilds can take a day or longer, depending on controller speed and workload. If another disk fails during the rebuild, then data is lost forever.

RAID 10
RAID 10 makes it possible to obtain an aggregated volume per stripe with a very good level of reliability (since it is based on replicated arrays). Since each cluster contains a minimum of two elements and a minimum of two arrays is required, a minimum of four storage drives are required to create a RAID 1 + 0 (RAID 10) volume.
Its reliability is high since all the elements of a cluster must be defective to cause an overall defect. The reconstruction is very efficient since it mobilizes only the disks of a single cluster and not all.
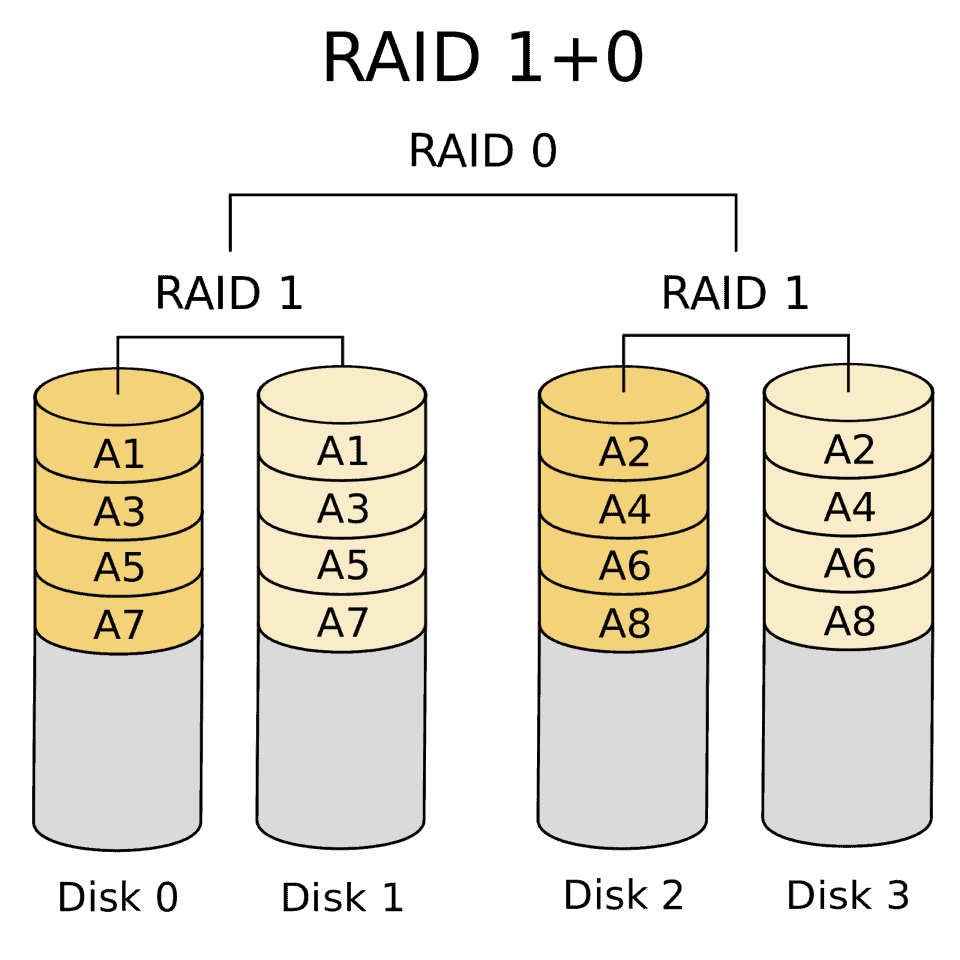
RAID 10
RAID 10 makes it possible to obtain an aggregated volume per stripe with a very good level of reliability (since it is based on replicated arrays). Since each cluster contains a minimum of two elements and a minimum of two arrays is required, a minimum of four storage drives are required to create a RAID 1 + 0 (RAID 10) volume.
Its reliability is high since all the elements of a cluster must be defective to cause an overall defect. The reconstruction is very efficient since it mobilizes only the disks of a single cluster and not all.

RAID 10
RAID 10 makes it possible to obtain an aggregated volume per stripe with a very good level of reliability (since it is based on replicated arrays). Since each cluster contains a minimum of two elements and a minimum of two arrays is required, a minimum of four storage drives are required to create a RAID 1 + 0 (RAID 10) volume.
Its reliability is high since all the elements of a cluster must be defective to cause an overall defect. The reconstruction is very efficient since it mobilizes only the disks of a single cluster and not all.

RAID 10 (DataCAM) VS. RAID 5 (standard)
Unlike the RAID 5 & 6 modes usually used in the market in order to reduce production costs, the RAID 10 mode writes two disk cylinders at the same time and is 65% faster in writing because no complex writing algorithm is used. At DataCAM, performance is always our priority.
RAID 10 (DataCAM) VS. RAID 5 (standard)
Unlike the RAID 5 & 6 modes usually used in the market in order to reduce production costs, the RAID 10 mode writes two disk cylinders at the same time and is 65% faster in writing because no complex writing algorithm is used. At DataCAM, performance is always our priority.
RAID 10 (DataCAM) VS.
RAID 5 (standard)
Unlike the RAID 5 & 6 modes usually used in the market in order to reduce production costs, the RAID 10 mode writes two disk cylinders at the same time and is 65% faster in writing because no complex writing algorithm is used. At DataCAM, performance is always our priority.
Table of the number of 8Kb / Sec files in writing
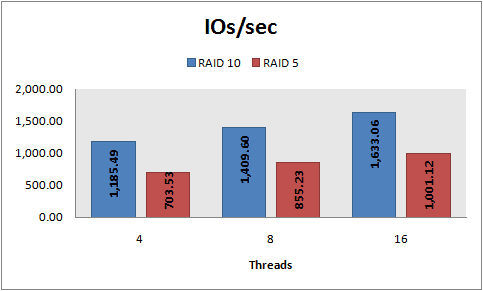
Write speed capacity table
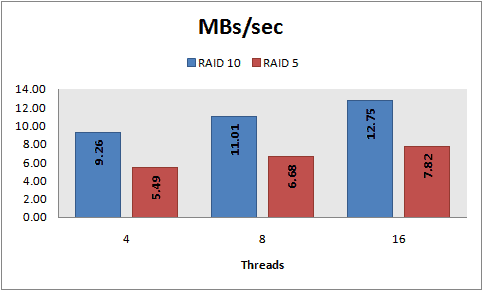
Latency table (waste of time)
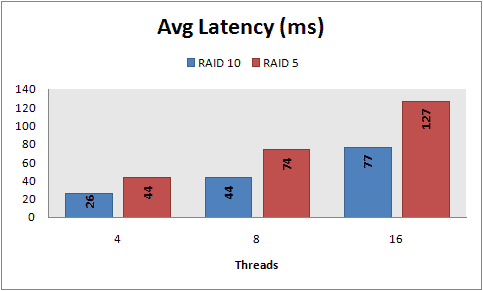
Number of 8Kb / Sec files in writing

Write speed capacity

Latency time (waste of time)

Number of 8Kb / Sec files in writing

Write speed capacity

Latency time (waste of time)


